Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and access management systems enable your organization to manage a range of identities including people, software, and hardware like robotics and IoT devices. With Identity and Access Management (IAM), administrators can set up and modify user roles, track and report on user activity, and enforce corporate and regulatory compliance policies to protect data security and privacy.
The Challenge
Today’s enterprise IT departments face the increasingly complex challenge of providing granular access to information resources, using contextual information about users and requests, while successfully restricting unauthorized access to sensitive corporate data. Below is the most well-known challenges that IT administrators face:
- An increasingly distributed workforce: with employees scattered all over a country or even the world, enterprise IT teams face a much more daunting challenge
- Distributed applications: with the increase of distributed applications comes an increase in the complexity of managing user identities for those applications.
- Productive provisioning: Without a centralized IAM system, IT staff must provision access manually. The longer it takes for a user to gain access to crucial business applications, the less productive that user will be.
- Bring your own device (BYOD): Nearly every company has some sort of BYOD policy. IT staff may struggle to manage who has access privileges to corporate data and which devices they’re using to access it.
- Password problems: when employees have trouble with their passwords, they most often contact IT staff for help, which can quickly and repeatedly drain important resources.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring support for processes such as determining access privileges for specific employees, tracking management approvals for expanded access, and documenting
The Solution
Identity and Access Management
Strong Identity and access management (IAM) solution can enable enterprises to boost employee productivity and bolster their overall security postures.
IAM becomes increasingly important to protect against outsider cyber threats and ensure that the right users have access to the right information.
IAM
Streamline user access
and secure data with Identity and Access Management solution
Making sure you provide appropriate access goes a long way in mitigating risks and improving the security posture of your organization. Start being proactive in your security approach.
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and access management (IAM) ensures that the right people and job roles in your organization (identities) can access the tools they need to do their jobs. Identity management and access systems enable your organization to manage employee apps without logging into each app as an administrator.
Identity and access management systems enable your organization to manage a range of identities including people, software, and hardware like robotics and IoT devices.
What is IAM Composed Of?
1.Single Sign-On
Single sign-on (SSO) is a form of access control that enables users to authenticate with multiple software applications or systems using just one login and one set of credentials. The application or site that the user attempts to access relies on a trusted third party to verify that the user is who they say they are, resulting in:
– Enhanced user experience
– Reduced password fatigue
– Simplified password management
– Minimized security risks for customers, partners, and vendors
– Limited credential usage
– Improved identity protection
2. Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication verifies a user’s identity with requirements to enter multiple credentials and provide various factors:
– Something the user knows: a password
– Something the user has: a token or code sent to the user via email or SMS, to a hardware token generator, or to an authenticator application installed on the user’s smartphone
– Something specific to the user, such as biometric information
3. Risk-Based Authentication
When a user attempts to log in to an application, a risk-based authentication solution looks at contextual features such as their current device, IP address, location, or network to assess the risk level.
Based on this, it will decide whether to allow the user access to the application, prompt them to submit an additional authentication factor, or deny them access. This helps businesses immediately identify potential security risks, gain deeper insight into user context, and increase security with additional authentication factors.
4. Data Governance
Data governance is the process that enables businesses to manage the availability, integrity, security, and usability of their data. This includes the use of data policies and standards around data usage to ensure that data is consistent, trustworthy, and does not get misused. Data governance is important within an IAM solution as artificial intelligence and machine learning tools rely on businesses having quality data.
5. Federated Identity Management
Federated identity management is an authentication-sharing process whereby businesses share digital identities with trusted partners. This enables users to use the services of multiple partners using the same account or credentials. Single sign-on is an example of this process in practice.
6. Zero-Trust
A Zero-Trust approach moves businesses away from the traditional idea of trusting everyone or everything that is connected to a network or behind a firewall. This view is no longer acceptable, given the adoption of the cloud and mobile devices extending the workplace beyond the four walls of the office and enabling people to work from anywhere. IAM is crucial in this approach, as it allows businesses to constantly assess and verify the people accessing their resources.
Why Do You Need IAM?
Companies need IAM to provide online security and to increase employee productivity.
- Security. Traditional security often has one point of failure – the password. If a user’s password is breached – or worse yet, the email address for their password recoveries – your organization becomes vulnerable to attack. IAM services narrow the points of failure and backstops them with tools to catch mistakes when they’re made.
- Productivity. Once you log on to your main IAM portal, your employee no longer has to worry about having the right password or right access level to perform their duties. Not only does every employee get access to the perfect suite of tools for their job, their access can be managed as a group or role instead of individually, reducing the workload on your IT professionals.
How Does IAM Work?
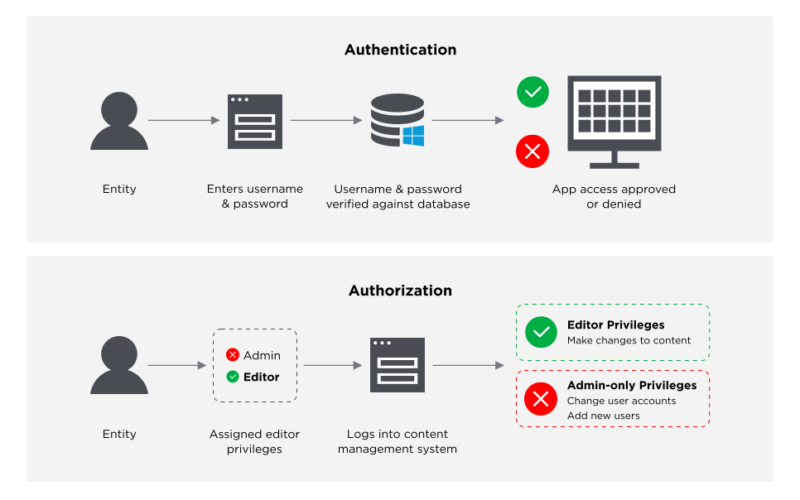
Identity management solutions generally perform two tasks:
- IAM confirms that the user, software, or hardware is who they say they are by authenticating their credentials against a database. IAM cloud identity tools are more secure and flexible than traditional username and password solutions.
- Identity access management systems grant only the appropriate level of access. Instead of a username and password allowing access to an entire software suite, IAM allows for narrow slices of access to be portioned out, i.e. editor, viewer, and commenter in a content management system.
IS IAM On-Premises or Cloud based Solution?
In the past, most identity and access management was managed by a server on the physical premises of an organization, which was called on-prem. Most IAM services are now managed by a provider in the cloud to avoid physical maintenance costs to the organization, as well as to ensure uptime, distributed and redundant systems, and short SLAs.




